Tutorial 4¶
Question 1¶
Step 1¶
def start_index(sequence):
n = len(sequence)
for i in range(n):
if sequence[i:i+3] == "AUG":
break
return i
rna_seq = "GCAUAUGUUCAUAUGAAUA"
j = start_index(rna_seq)
print(j)
4
Step 2¶
def translate(codon):
genetic_code = ["GCA", "GCC", "GCG", "GCU", "UGC", "UGU", "GAC", "GAU", "GAA", "GAG", "UUC", "UUU", "GGA", "GGC", "GGG", "GGU", "CAC", "CAU", "AUA", "AUC", "AUU", "AAA", "AAG", "UUA", "UUG", "CUA", "CUC", "CUG", "CUU", "AUG", "AAC", "AAU", "CCA", "CCC", "CCG", "CCU", "CAA", "CAG", "AGA", "AGG", "CGA", "CGC", "CGU", "CGG", "AGC", "AGU", "UCA", "UCC", "UCG", "UCU", "ACA", "ACC", "ACG", "ACU", "GUA", "GUC", "GUG", "GUU", "UGG", "UAC", "UAU", "UAG", "UAA", "UGA"]
amino_acids = ["A", "A", "A", "A", "C", "C", "D", "D", "E", "E", "F", "F", "G", "G", "G", "G", "H", "H", "I", "I", "I", "K", "K", "L", "L", "L", "L", "L", "L", "M", "N", "N", "P", "P", "P", "P", "Q", "Q", "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "R", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "T", "T", "T", "T", "V", "V", "V", "V", "W", "Y", "Y", "!", "!", "!"]
i = genetic_code.index(codon)
aa = amino_acids[i]
return aa
x = translate("AAA")
print(x)
K
Step 3¶
def translate_sequence(sequence):
j = start_index(sequence)
n = len(sequence)
result = ""
for i in range(j, n-3, 3):
codon = sequence[i:i+3]
if codon == "UAG" or codon == "UAA" or codon == "UGA":
break
else:
result = result + translate(codon)
return result
rna_seq = "GCAUAUGUUCAUAUGAAUA"
aa = translate_sequence(rna_seq)
print(aa)
MFI
Step 4¶
rna_1 = "CAACAAUGCUCCCCGCCUAGUUG"
print(translate_sequence(rna_1))
rna_2 = "UAAAAUGAAUAAUAGAUAA"
print(translate_sequence(rna_2))
MLPA
MNNR
Question 2¶
The answer below includes only the English and French languages. It is not difficult to extend to further languages.
How might you extend to an arbitrary number of languages…?
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
freq_french = [7.60, 0.96, 3.39, 4.08, 14.47, 1.12, 1.18, 0.93, 7.21, 0.30, 0.16, 5.86, 2.78, 7.32, 5.39, 2.98, 0.85, 6.86, 7.98, 7.11, 5.55, 1.29, 0.08, 0.43, 0.34, 0.10]
s = sum(freq_french)
# ensure the sum is 1
for i in range(26):
freq_french[i] /= s
freq_eng = [8.34, 1.54, 2.73, 4.14, 12.60, 2.03, 1.92, 6.11, 6.71, 0.23, 0.87, 4.24, 2.53, 6.80, 7.70, 1.66, 0.09, 5.68, 6.11, 9.37, 2.85, 1.06, 2.34, 0.20, 2.04, 0.06]
s = sum(freq_eng)
# ensure the sum is 1
for i in range(26):
freq_eng[i] /= s
with open("french.txt") as f:
text = f.read()
alphabet = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
counts = [0] * 26 # this syntax creates a list containing 26 zeros
text = text.lower()
for c in text:
i = alphabet.find(c)
if i > -1:
counts[i] += 1
s = sum(counts)
for i in range(26):
counts[i] = counts[i] / s
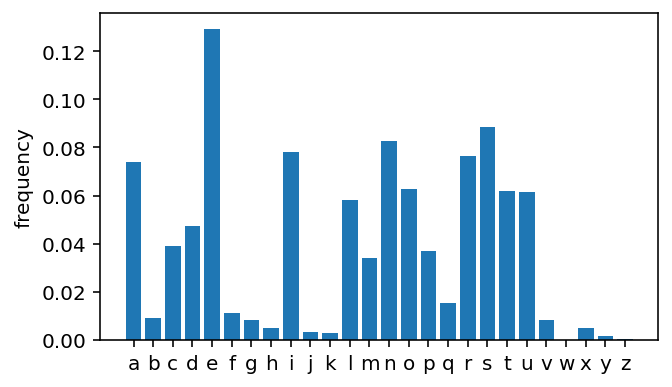
plt.figure(figsize=(5,3))
plt.bar(list(alphabet), counts)
plt.ylabel("frequency")
sim_eng = 0
sim_french = 0
for i in range(26):
sim_eng += (freq_eng[i] - counts[i])**2
sim_french += (freq_french[i] - counts[i])**2
m = min(sim_eng, sim_french)
if m == sim_eng:
print("English")
elif m == sim_french:
print("French")
French